Prostatitis is the most common urological pathology in men of reproductive age. According to surveys, each third of them at least once in his life experienced symptoms that could be interpreted as inflammation of the prostate gland. Despite such a high appearance of pathology, prostatitis remains a poorly studied disease.To date, there is no consensus that becomes an initial factor of inflammation because it is possible to distinguish the pathogens of STIs from the genitourinary tract of patients in only 10% of cases.

The lack of clear diagnostic criteria and the characteristic signs of the disease complicate the calculation of patients. Symptoms of prostatitis are so nonspecific that each physician interprets them with a large part of the subjectivity and can attribute it to a completely different pathology. Therefore, the approach to treatment also varies and often patients wander from one hospital cabinet to another without any positive dynamics for years. Prostate deprives a man of confidence in his sexual power, put his thoughts on a problem, and brings him not as much physical as psychological suffering.
What is a prostate and why is it necessary?
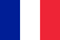
The prostate gland (prostate) is a small gland of a man around the urethra below the bladder. It tightens the urethra, forming one of its sphincters - a muscular outlet created to maintain urine. In its shape and size, the prostate resembles a chestnut nut, which is often compared to anatomists. The part of the urethra, which passes inside the gland, is called prostatic. Its convex posvex of the prostate is in contact with the rectum, so it can easily be felt with an examination of the rectal finger. The anterior surface of the gland is close to the pubic node and is associated with it to the movement of connective tissue ligaments, and the venous plexus extends between them.
The prostate gland consists of lobules, each of which is made of alveoli - small bags coated with secret epithelium. The alveoli are interconnected by the outlet channels in the form of tubes, which join each other, enlarge and eventually fall into the simple part of the urethra. Within the secretory bags, the prostatic fluid is synthesized and accumulated, which includes nutrients for sperm. It allows male sex cells to maintain its activity in the female body for up to 5 days, which significantly increases the chances of fertilization.
Enlightenment of the gland occurs at the time of the shed. The prostate juice is mixed with the secret of the testicles and accounts for 10 to 30% of the final volume of the sperm. Thus,The prostate gland performs 2 main functions in a man's body:
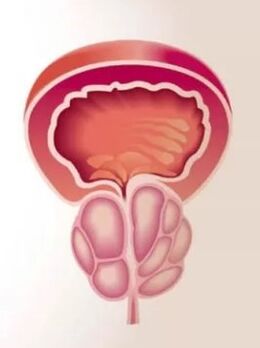
What is the disease developing?
Prostatitis is inflammatory changes in the prostate gland and it should be understood that they arise not only under the influence of the bacterial microflora.The causes of inflammation can be any factor that leads to damage to the glandular tissue and the destruction of its cells.
As in any other tissue, the inflammatory process in the prostate continues through certain stages:
For the proposed reason, the prostate is divided into:
How does the disease appear?
Easier to diagnose acute prostatitis,which continues with signs of pronounced intoxication and inflammation. In a human, the temperature rises significantly to 38-39 degrees C, pronounced pain in the perineum, in the rectum area appear. They can give in the groin, in the testicle, in the penis, and be as unbearable as a man's daily activity is harshly worried. In some cases, the body temperature measured in the axillary cavity does not pass the normal indicator, but the rectal will in any case be 1-2 degrees for normal. Signs of prostate also become a violation of urination: severe urination requirements, after which it is impossible to inhibit or an acute delay in the urine due to severe gland edema. Sometimes the defecation becomes painful, as the magnified prostate in size adheres to the rectum lumen.
Chronic prostatitisIn its manifestations, it is so diverse that it can be easily confused with another pathology. In the most typical cases, the symptoms of prostatitis occur:
As a rule, with chronic prostatitis, a person's overall well -being does not worry, body temperature is maintained normal throughout the disease.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis is determined by a doctor's urologist or andrologistAfter examining the patient, collecting an anamnesis and studying symptoms. The doctor should detect the method of patient contraception, the presence of STIs in a sexual partner, the possibility of anal contacts without condoms. These data facilitate the diagnosis and direct the doctor's thoughts in the right direction. The recipe for the symptoms of the disease or disturbance in the perineum allows us to judge the flow of prostate and its severity. The urologist necessarily examines the patient's genitals and performs a rectal examination of the prostate gland. To do this, he inserts a finger into the patient's back passage and grabs the elongated prostate on the front wall of the rectum. Its pain and size indicate the intensity of the inflammatory process.
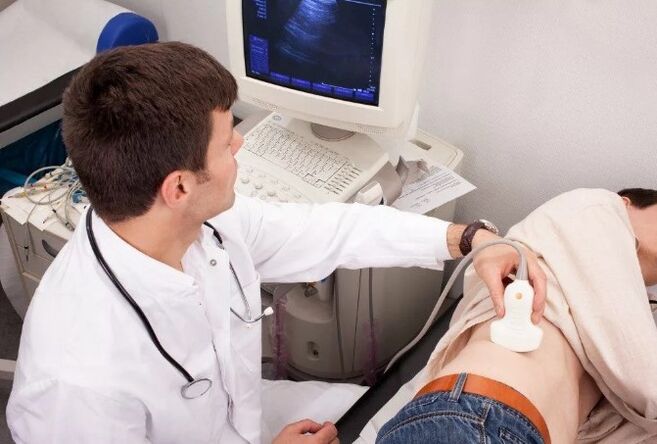
Further, the doctor performs a number of instrumental, microscopic, bacteriological and immunological studies in order to clarify the cause of the disease. The most common diagnostic method is the 4 or 3-cell urine sample. The first method is more time and difficult to practice in practice, as it requires the patient to consciously interrupt urination. The second modification is simpler: the patient constantly urinates in three different containers in equal parts. The first part talks about the condition of the urethra, the second about the bladder and kidney pathology, from the third, information is obtained on the condition of the prostate gland. All the collected material is studied under a microscope. With prostatitis in the third part of urine, leukocytes and sometimes bacteria are found.
Access to the study of prostate and massage when collecting secrets
For microscopy, the secret of the prostate gland is also taken. To do this, the doctor performs a prostate massage through the rectum wall for some time in order to empty into the urethra. Smops are made of material collected in the lab, painted and studied under a high growth. One sign of inflammation are leukocytes, bacterial etiology of the disease - bacteria in a stain. To determine the type of pathogen, the secret of the prostate is planted in the nutritional media. If pathogenic microorganisms are present in it, then after 3-5 days they form microbial colonies, which can then be studied by the bacteriological method allow you to obtain data on microflora's sensitivity to antibiotics.
Of instrumental diagnostic methods, :

Starting the treatment of chronic prostate, you should allocate in a long war, as it is not always possible to cure it within weeks or even months. It is recommended to combine various methods and tools for therapy, it is useful to improve medication therapy with households. With stagnant prostate, regular sex is needed, interrupted sexual acts are unacceptable. The patient's psycho -emotional background is important: depression, depression, problems in personal life and sexual spheres are able to deny all the efforts of doctors.
How to prevent?
Prostatitis prevention includes:
Despite the fact that today prostate is not associated with the risk of developing adenoma or prostate cancer, the disease brings a lot of suffering to its owner. A man tired of chronic pain, feeling his sexual weakness, tired of prolonged treatment, varies significantly from the outside and experienced doctors determine such patients at first sight. To avoid such fate, you need to be careful about your health, carefully protected with any new partner and treat sexually transmitted diseases in time. Prostatitis is not fully treated in all cases, but an experienced urologist is able to significantly improve the patient's condition and the quality of his life.